Dialog Insight collects a lot of data natively, including clicks and openings in an email, with the purpose of measuring campaigns' performance. By default, this data is linked to contacts who interact with your content and can be used in order to target these contacts or compile statistics.
However, collecting data is getting more enforced by laws (GDPR and Law 25) that require the possibility for a contact to withdraw from the automated collect in any form. Dialog Insight offers, in this sense, a system to allow the contacts to withdraw from the behavioral tracking in the communications (clicks, openings, etc.) for all channels. This option anonymizes the behaviors but does not affect the statistics on your communications. The actions will not be linked to a contact. In that manner, the contacts' statistics will display how many contacts did an action anonymously.
Behavioral tracking works similarly to opt-in management: the module adds fields to the project in order to track the consent status of the contact and the consent history for the purpose of auditing. The module also features opt-out methods. When sending messages, tracking consents will apply automatically.
Acces path: Project → Other configurations |
Step 1: Activate Behavioral Tracking
Follow the access path and activate the Behavioral tracking and data protection module:
| If you have a CDP structure, make sure to activate the behavioral tracking in the project you use to send your communications. |
By activating the behavioral tracking module, it generates essential tables and fields for tracking contacts' consent, including 2 administrative fields for contacts:
- hasTrackingConsent - Tracking consent: True/False type field
- dtTrackingConsent - Date of tracking consent
By default, contacts who did not withdraw from tracking will be tracked (opt-out mode). If you prefer, you can toggle to opt-in mode to force tracking only on contacts who opted-in.
You can change the default method. First, go to the configuration menu and click on Edit:
Then, select the method you want to use: 
Step 2: Configure the Tracking Consent Interception
The interception feature is optional. When this feature is activated When a contact clicks on one of the links inside your emails (except for communication types you choose to exclude), a form is displayed to ask if the contact accepts or refuses the collection of behavioral data.
Configuring the interception is done in 2 steps. First, you must define the interception conditions (delay between interception, communication types to exclude). Second, you will customize the interception form for English and for French (if it applies). If you have other languages for your communications, you can create a form for each of these languages.
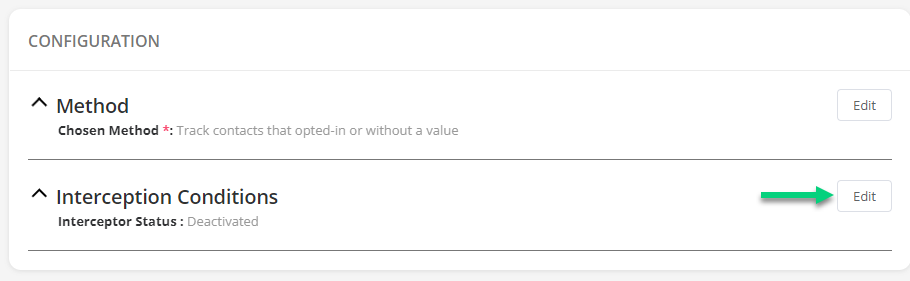
Then, click on Activate interception and set the interception conditions:
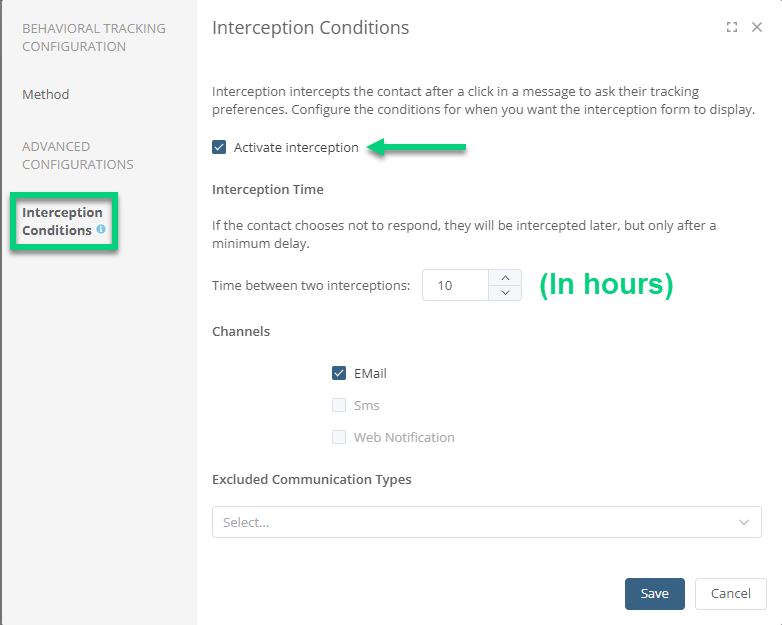
- Interception Time: Indicate the delay in hours between interceptions.
- Channels: At the moment, the only channel available is Email. Stay tuned for the opening of other channels! :-)
- Excluded Communication Types: By default, interception applies to all communication types, except if you select here a communication type to exclude.
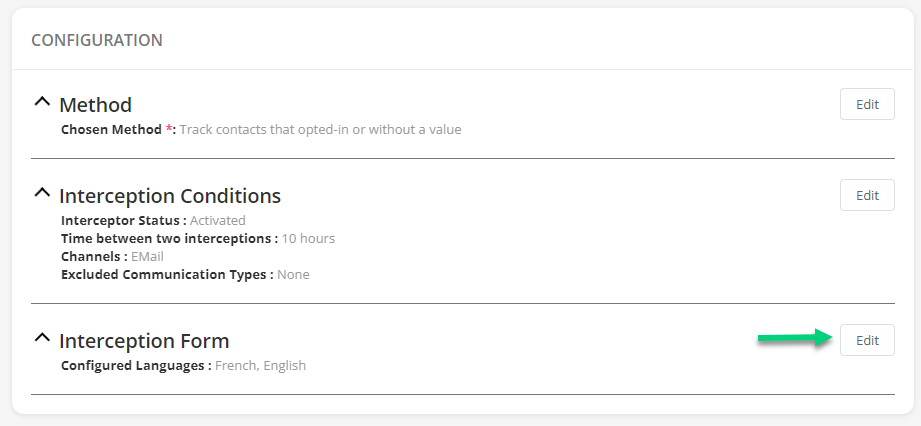
You can edit the default forms for English and French depending on the languages you use in your emails:
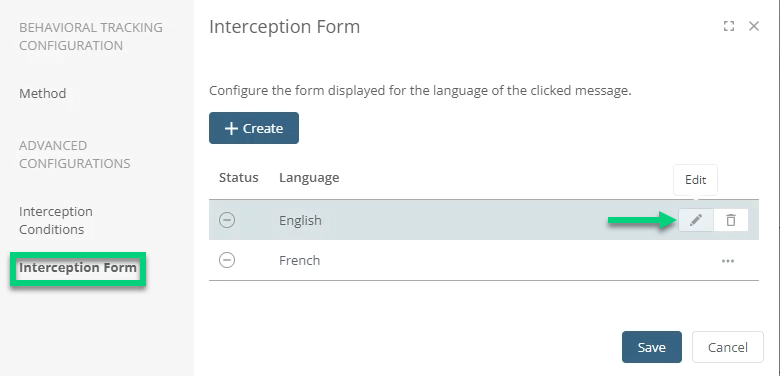
If you have emails using other languages, you can create a new form for these languages by clicking on Create. Customize content to adapt it to your use of behavioral tracking:
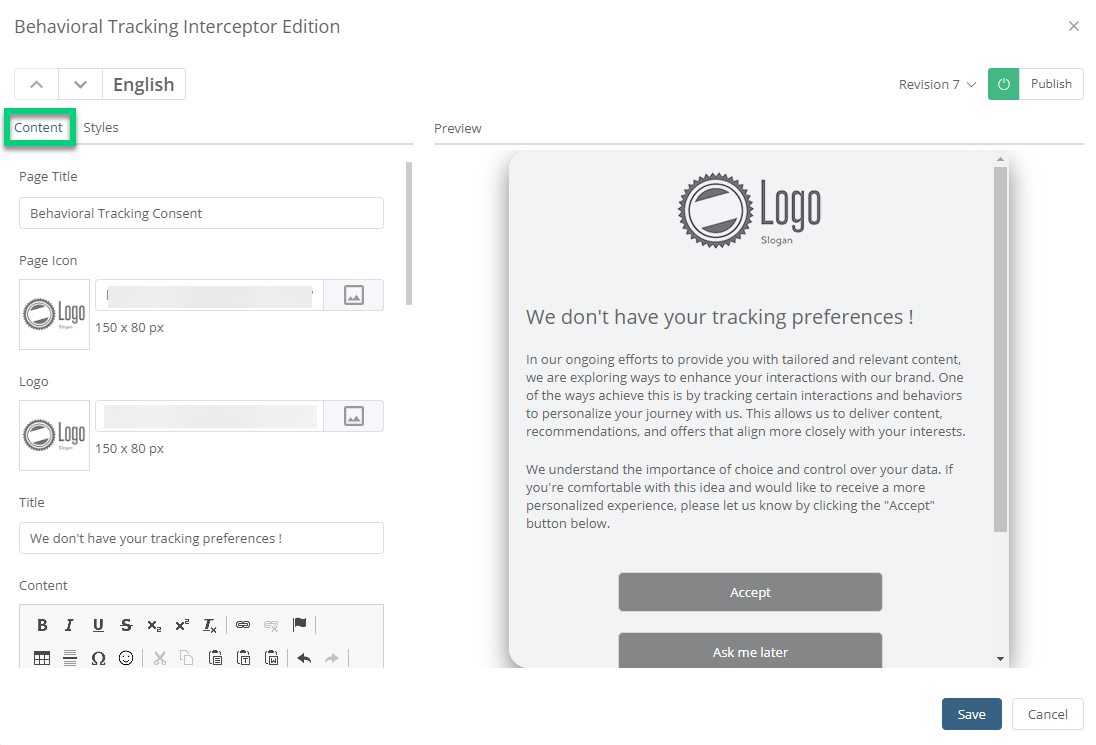 Change titles, add your logo and adapt the legal text to your context of data use.
Change titles, add your logo and adapt the legal text to your context of data use.Buttons are linked with the administrative fields for consent hasTrackingConsent and dtTrackingConsent. These fields are generated when you activate the behavioral tracking module. When a contact clicks on Accept, the value of the hasTrackingConsent field changes to Accepted. If the contact chooses Ask me later, an interception will be sent again later depending on the delay defined in the interception conditions.
To finish, change the styles by adding the colors of your brand:
Step 3: Import Consents
If you use the interception, you can wait for consents to come in through the interception form. Otherwise, you have 2 other options to add tracking consent.
| Consent for behavioral tracking must not be confused with consent for communications. If interception for behavioral tracking and for communication consent are both configured, in theory, they should not be in conflict. If both are activated and are supposed to be displayed to the contact, opt-in consent will be prioritized, then behavioral tracking consent will be presented at the following click. |
If you host tracking consents in an external system, you can do a manual import with an Excel or CSV file. You can use administrative fields (hasTrackingConsent and dtTrackingConsent) for mapping or importing the updated status of tracking consents. The consent will be accepted if the consent date is not a greater value than the field at the moment of the import in order to not overwrite an up-to-date status.
If you use opt-in or profile update forms, you could insert an input to ask for tracking consent. In the configuration of the form, add a field for tracking consent: 
Step 4: Create an Opt-out Form
Ensure to offer an opt-out option for behavioral tracking by configuring one of these 2 options.
The behavioral tracking opt-out form allows contacts to unsubscribe from cookies in your email communications. A link to this form can be inserted in your messages, from the Link library. You can also add a link to this form in your current opt-out, opt-in and profile update forms.
When activating the module, a Behavioral Tracking opt-out section is generated. In this section, you can configure the form styles and content. You can integrate the link to the form in your communications.
You can also give the option to contacts to withdraw from behavioral tracking using the opt-out process. In the opt-out form editor, click on Offer the option to opt-out from behavioral tracking: This option will display a text at the bottom of the opt-out form with a link to the behavioral tracking opt-out form.
This option will display a text at the bottom of the opt-out form with a link to the behavioral tracking opt-out form.
Results
Status and Consent History for a Contact
Behavioral tracking status is displayed in the contact's profile: Accepted, Refused or Unanswered.
The status appears in the Admissibility and Consent section: For more details, click Consult History.
For more details, click Consult History.
In the contact's profile, contacts who refused tracking will be identified as non-targeted by the message sending. It is impossible to see if the message was sent to these contacts.
Sending results
You do not need to set additional configurations for message sendings. The system automatically applies behavioral tracking conditions for contacts. In the results, since the tracking data are from anonymous contacts, global results are not affected. However, contacts who refused to be tracked are not included in the list of contacts, but they will be counted in the total of contacts in the legend and will be identified as untracked contacts.
Injection Rules
When Behavioral tracking and data protection feature is enabled in a project, a new option is added to the configuration parameters of an injection rule that allows you to prevent the rule from being applied to contacts who do not wish to be tracked. You should know that not all injection rules have to be restricted to tracked contacts. Make sure to enable this option for each rule you want to apply it to. To learn more about injection rules, see this article.
Targeting
As mentioned at the beginning of this article, Dialog Insight captures actions and uses them to target contacts. This type of targeting is often used for re-engagement or loyalty campaigns. However, contacts who refused behavioral tracking are considered as not targeted by sendings. This way contacts who refused are excluded from this type of targeting. Moreover, since sendings are not attached to a contact, segmentation tools will not work for these contacts
When a contact is not tracked, behavioral clauses (in tools like Groups or Scoring) which rely on this information will not be able to target contacts who refused tracking. For automated campaigns as well, conditions for behavior will exclude contacts.
BI Tools
Since sendings are anonymized at the source, you will be able to use segmentation of sending results with contacts' criteria.
The potentially affected tools include:

