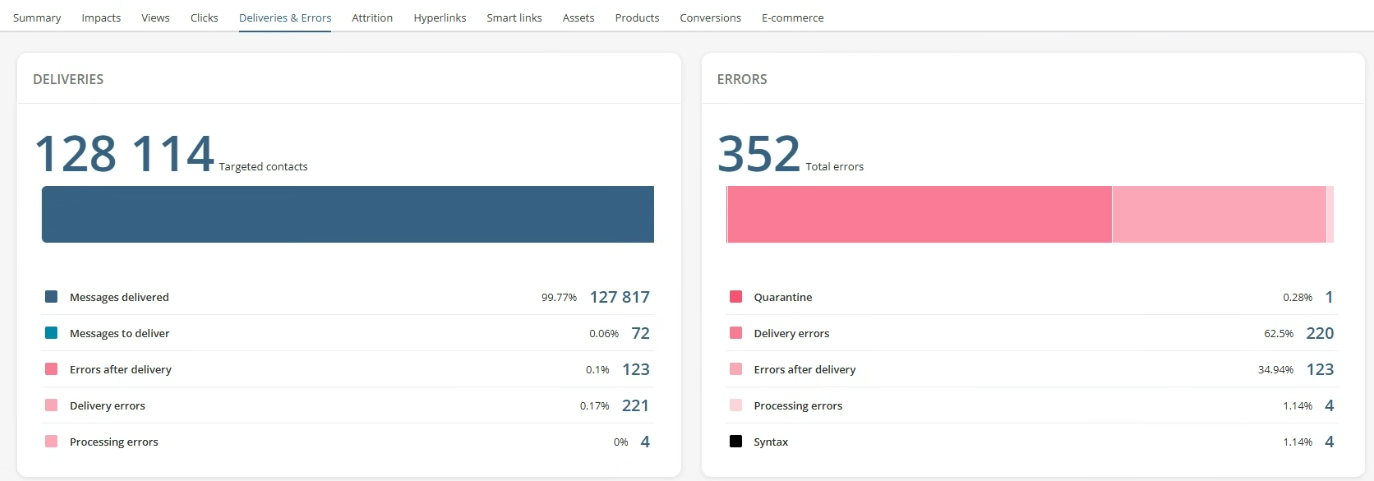
In the Email Analytics page, Dialog Insight divides delivery errors into different categories:
- Quarantine
- Delivery errors
- Errors after delivery
- Processing errors
In all cases, it implies messages that have NOT reached the recipient. The actual number of errors is therefore the total of those categories. The difference between the error types is based on how and when the error was detected.
Quarantine
When a delivery fails due to a full mailbox or an invalid email address, the recipient (contact) is quarantined to prevent future unsuccessful attempts. The issue must be resolved for these contacts (address updated, deletion, or manual reactivation) before they can be targeted again.
Quarantine is a temporary status given to a contact that prevents messages to this contact, without, however, deactivating or unsubscribing the contact permanently. The contact's preferences and subscriptions remain valid. Correcting the email address (either by import, profile update form or directly in the contact's profile) will lift the quarantine to make the contact eligible again to receive messages.
→ Lifting a contact's quarantine
Delivery Errors
A delivery error occurs when the recipient's mailbox provider refuses the message at the time of the sending. In this case, the email is never transmitted to the contact and the sending is immediately considered an error.
Principal causes:
- Non-existent or invalid address: The domain or address does not correspond to any real server or account.
- Mailbox is full: The recipient's inbox has reached its capacity limit.
- Server rejection: The server temporarily or permanently refuses to receive the message (for example, due to a spam filter or domain configuration).
- Domain problem: The domain of the address no longer exists or does not have an active mail server.
- Content or format error: The message is too large or contains blocked elements (attachments, links, etc.).
Errors After Delivery
A post-delivery error occurs when the recipient's server initially accepts the message, but an error is detected afterward. In this case, the message initially had a delivered status, but a bounce was later received, indicating that the email ultimately did not reach the contact's inbox.
It's also important to know that the time between initial delivery and the return of this message is unpredictable and potentially very long (typically up to several days), as the intermediate server may have attempted to deliver the message for several days before returning it to Dialog Insight's servers. This is why the number of errors after delivery can continue to increase even after the campaign has ended.
When a message goes through an additional transmission and is ultimately not delivered, it is considered an error. However, since this message has already been recorded as delivered (at the first delivery server), this data is already included in reports and contact histories. To prevent delivery results from fluctuating over time (the number of delivered messages decreasing over time) and to prevent the total number of deliveries and errors from exceeding 100%, Dialog Insight separately tracks errors resulting from messages returned to the sender.
Error feedback can arrive several hours or days after sending. This is why the number of errors after delivery can continue to increase even after the campaign has ended.
Processing Errors
These are messages that have not been built properly, often in the case of personalized content that cannot be displayed for one or more contacts, or missing conditions or data.
| Resources |

